In finance and investing, you indeed heard about a term called Equity. The Stock Market is also known as the ‘Equity Market‘. So a question may arise in your mind: What is equity in the business? We believe the concept of equity is a piece of essential knowledge for everyone, especially for investors who want to measure the value of a Business. In this article, we are going to discuss and explain all about what is Equity in Business, the types of equity, how to calculate it, and many more.

What is Equity in Business?
In a business, equity represents both ownership and worth of that business. For investors Equity is an indicator that measures the financial health of a company or business.
In simple words, Equity represents the amount of money that would be returned to a company’s shareholders if all assets of a business were liquidated and all of the company’s debts were paid off.
We can say the total equity of a company represents its total valuation in a market. Further depending on the financial health of a company equity can be positive or negative.
Negative equity is a red flag to a particular business which means said business is in massive loss and has high debts in comparison to its all assets.
On the other hand, Positive equity means a business is in profit and has more assets than debt, and shows growth potential of a business.
How Do You Calculate Business Equity?
To calculate the equity all the required financial metrics are available on the company’s balance sheet. The following simple formula is used to calculate the equity of a business:
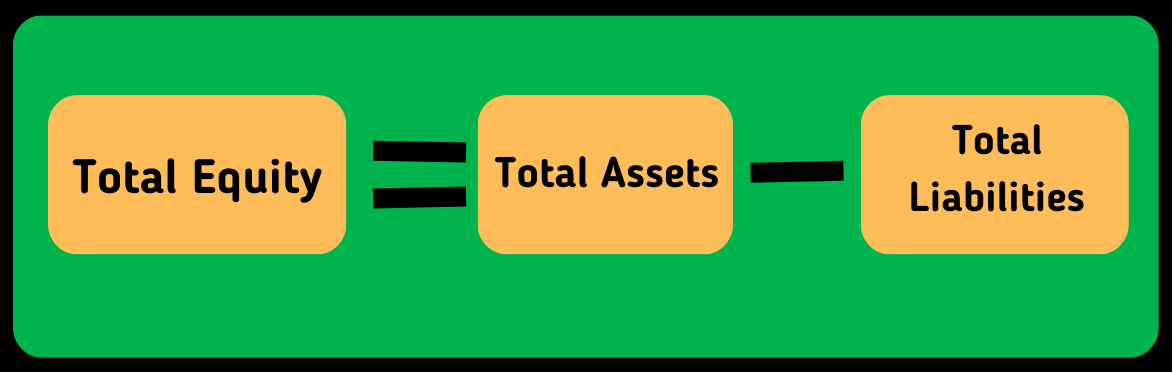
Keep in mind that this formula includes both current and noncurrent assets and liabilities.
This equation can be further used to determine assets and liability by rearranging the formula as given below:

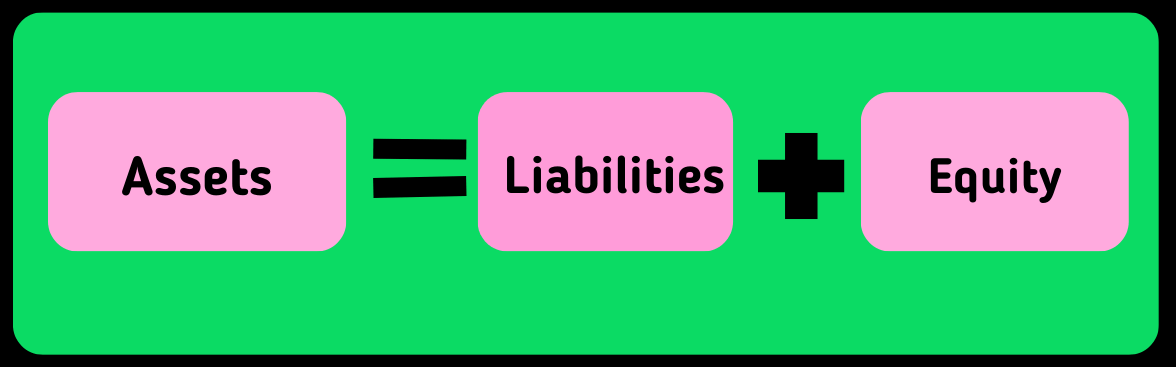
Here are examples of some common assets and liabilities.
Examples of Assets | Examples of liabilities |
Inventory | Loans
|
Property, plant, and equipment
| Accounts payable operations. |
Accounts receivable (AR)
| Bank debt
|
Cash
| Taxes owed |
Raw materials
| Mortgage debt |
Trademarks and patents | Employee Wages Expenses. |
👉Read More: Strategic Asset Allocation | The Ultimate Key to Wealth Creation
What is Debt-To-Equity (D/E) Ratio?
While discussing “what is equity in a business” you must also know about Debt to Equity Ratio because this Debt to Equity ratio plays an important role while analyzing the financial health of a business and it helps a potential investor to know if a particular business is using equity financing or debt financing to run its operations.
The D/E ratio can be calculated by using the following formula:
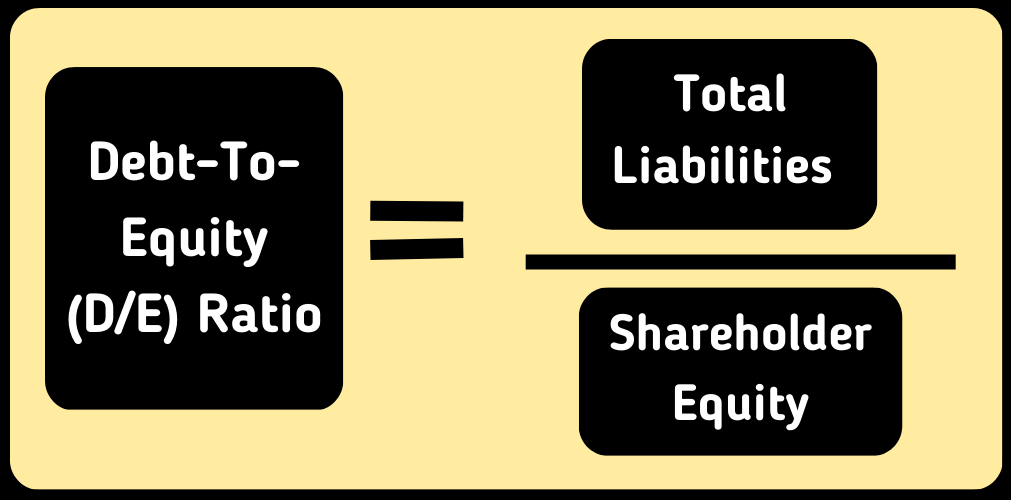
Here total liabilities mean all liability that a business owes and Shareholder’s Equity represents the net asset that a company owns. Net Asset can be derived using the following formula
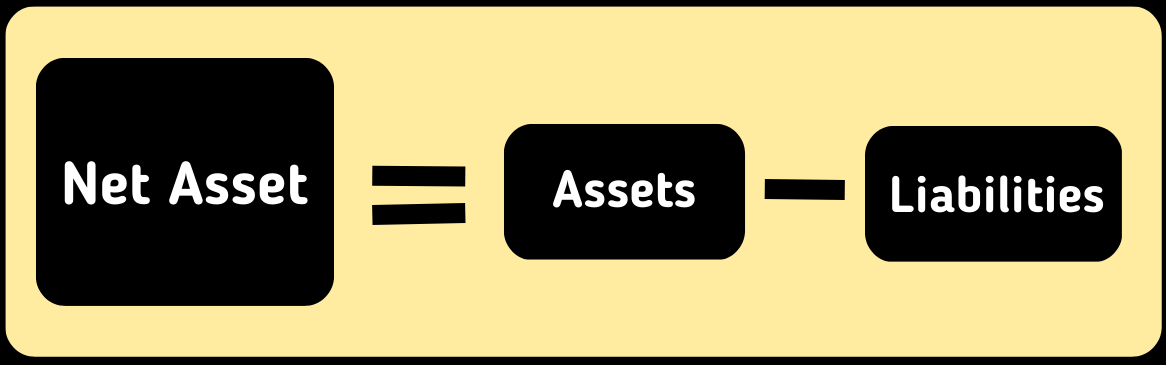
You can find all the information about assets and liabilities on the company’s balance sheet. If a business is already listed in the stock market then you can easily find the balance sheet of the company through online tools/sites like yahoo finance. For your better understanding here we attached a screenshot of amazon.com below:

- High Debt to Equity Ratio:
A high D/E ratio is a sign of high risk which represent that business is borrowing more money to run its operation rather than using its own money.
- Low Debt to Equity Ratio:
A low D/E ratio means a business has more owned capital than borrowed capital and has excess shareholder’s equity and has no need to take debt to run its operations.
There are many online tools/websites available like ycharts.com where you can easily find the debt-to-equity ratio. For example, we have attached a screenshot of debt to equity ratio of Apple shares as follows
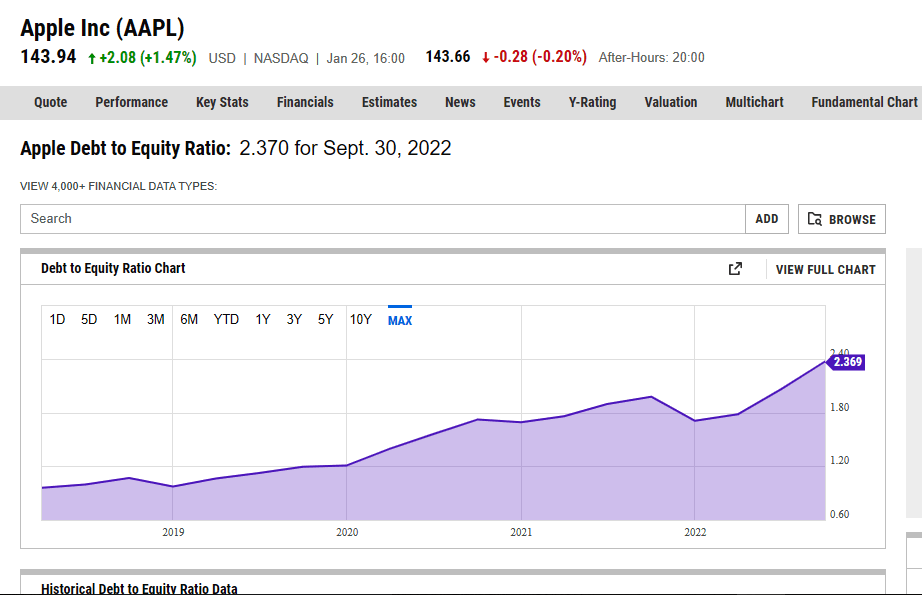
Misnomers in the interpretation of the D/E ratio.
As we have already discussed above that Debt-To-Equity (D/E) Ratio is a crucial financial metric to analyze the health of a business and a high D/E ratio indicates the bad financial health of a business. In contrast, a Low D/E ratio represents the good financial health of a business.
But it is not always true. Its true interpretation depends upon the nature of a business/industry. Depending upon the nature of businesses high D/E ratio may be common in some and in some other businesses, a low D/E ratio may be common.
For Example High capital-intensive businesses like manufacturing generally have high D/E because to run such types of businesses intensive capital is required and there is nothing wrong with it. whereas businesses like services and technologies are low capital intensive and may commonly have a low D/E ratio.
So always keep in mind the nature of business while analyzing it through the Debt-to-equity ratio and also analyze another financial metric like OCF.
What are The Types of Equity?
If you have read the above article carefully then now you understand the concept of ‘what is equity in business’ means and how you can calculate it? But ‘Equity’ is a general term and there are other several types of equities that exist. Let’s discuss them one by one for more insight.
-
Owner’s Equity:
Owner’s equity represents the right of the owner in business assets if a company is a privately owned sole proprietorship. A potential investor use owner’s equity calculation to find out the valuation of a Business/company. It could be easily understood by the following equation.
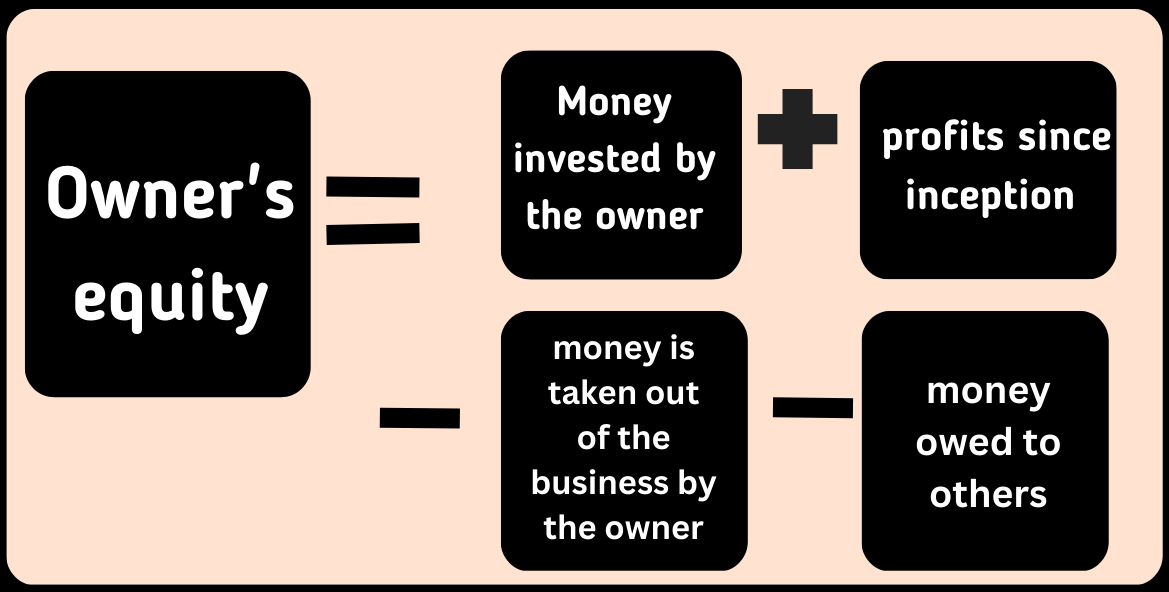
The owner’s Equity is not shown as an asset on the balance sheet of the company. Because owner’s equity is an asset of the business owner, not the business itself.
-
Shareholder’s Equity:
Shareholder’s Equity is also known as stockholder’s equity. It refers to the share held by the company’s investors or shareholders if a business is structured as a corporation. In this case, many investors have a stake in a business, and the business owner does not have 100% equity ownership.
In a Corporation type business Shareholder’s Equity and Owner’s Equity is the same thing and include the following type of Financial instruments:
- Common stock: These are also known as traditional shares and represent the ownership or stake in a business. This type of stockholder is entitled to voting rights and dividends.
- Preferred stock: This type of stock gives a fixed dividend with a payment that is prioritized over common stock to the stockholders.
- Retained earnings: It means Profits earned to date – any dividends that have already been paid out.
- Treasury stock: Treasury Stocks are those stocks that a company has reacquired from shareholders.
How To Calculate Shareholders’ Equity?
In a large corporation Owner’s Equity and Shareholder’s equity is the same thing because the owner is also the shareholder of a business, the only difference is that owner holds more equity than other shareholders.
Many investors use the share capital method to calculate shareholder equity and also known as the investor equation. Let us understand the investor equation as given below:

Here Share capital means the total money raised by a business through issuing common and preferred stocks
Retained Earing represents a business’s total earnings after accounting for the dividends.
Treasury stocks are those stocks that have a company bought back or reacquired from retail investors.
-
Private Equity:
Private Equity terms generally refer to those businesses which are not listed in the public market/stock market. These Privately held companies can sell off their shares directly to investors to raise the money before listing and investors become partners to that business. These private equity investors are pension funds, insurance companies, or accredited individuals.
-
Home Equity:
Home equity simply means how much value the home property that the owner of a business owns. Home equity is the greatest source of individual collateral. It can be calculated by subtracting the remaining mortgage payments from the value of the home property.
-
Brand Equity/Intangible Equity:
For a larger corporation, a business has both tangible and intangible assets. Tangible equity refers to the value of physical assets like machinery, plants, product inventory, and real estate possession.
Intangible assets are non-physical assets of a business which include the business’s Brand value, reputation, intellectual properties, and brand identity.
The value of these intangible assets of a business commonly refers to as intangible Equity or Brand Equity.
What is Equity Financing?
Most small businesses or startups are founded by business owners with their own capital/savings. In order to expand their new business more funds are required and business owners can raise funds either by borrowing from banks called ‘debt financing’ or by selling company shares to angel investors or venture capital is known as ‘Equity Financing‘. Equity Financing is a popular technique to raise funds because at the initial state, businesses are new and banks would face problems evaluating the valuation of new businesses.
What are The Advantages and Disadvantages of Equity Financing?
Here quickly we discuss some pros and cons of Equity financing in an easy way.
Advantages of Equity financing:
If a new business or startup got failed then the business’s owner would not have to pay any money to the investors.
If a new Business finds the right investors then the business would able to connect with other various professionals in the industry and could apply their expertise in new business.
In equity financing, businesses don’t have to pay interest whereas in debt financing interest has to pay to banks.
Disadvantages of Equity financing:
Equity Financing is a very common and popular method amongst new startups to raise funds but it has its own disadvantages also.
In Equity Financing, a business owner have to sell a part of the ownership of his business to the investors to raise funds which means the decision-making power of the owner also decreases.
Sometimes Equity Financing takes a longer time to find the right investor to raise funds in comparison to getting a loan from a bank.
Equity vs. Return on Equity.
As we have seen What is equity in business means and equity has various meanings but in simple words, it represents an ownership stake in a business or company like a shareholder owing equity.
Whereas Return on equity (ROE) is an important financial metric. ROE measures financial performance and can be calculated by dividing net income by shareholder’s equity. ROE could be considered as a return on the net asset because shareholder equity is equal to the business’s assets minus debt.
ROE tells potential investors how effectively management uses a business’s assets to create profit. We can also say that Return on Equity (ROE) measures how much profit is generated from a business’s shareholder equity.
You can find all the financial metrics including ROE from online tools/sites like zacks.com, Yahoo Finance, etc. Here we have provided a screenshot of the ROE ratio of Tesla below for your better understanding:
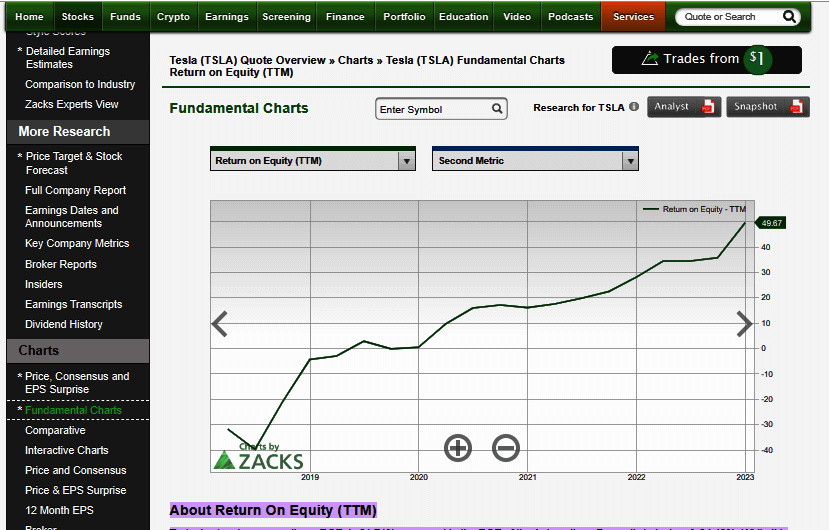
Conclusion.
In this article, we have discussed in depth What is equity in business means and what is its significance in a business. In a business, equity represents both ownership and worth of that business and behaves like a crucial financial indicator to measure the financial health of a business. In this article, we have discussed its various types, equations, and various financial metrics like ROE, and D/E ratio which commonly come with the term Equity. Hope, you will like our efforts and feel free to provide us feedback for further improvements.
FAQs
What Exactly is Equity?
Equity represents the stake of ownership in the business assets of shareholders. In simple words, Equity represents the amount of money that would be returned to a company’s shareholders if all assets of a business were liquidated and all of the company’s debts were paid off. There are 5 types of Equities that exist in business:
- Owner’s Equity
- Shareholder’s Equity
- Private Equity
- Home Equity
- Brand Equity
What is Equity in a Business?
Equity in a business represents its total valuation in a market. In a business, equity represents both ownership and worth of that business. For investors Equity is an indicator that measures the financial health of a company or business. Further depending on the financial health of a company equity can be positive or negative.
Negative equity is a red flag to a particular business which means said business is in massive loss and has high debts in comparison to its all assets.
On the other hand, Positive equity means a business is in profit and has more assets than debt, and shows growth potential of a business.
Is Equity Real Money?
No equity is not real or hard money but it is an asset like your owned car or home. It means someone has an ownership stake in a business and like all other assets, equity would also give you money after selling it.
What is The Difference Between Capital and Equity?
Capital
| Equity |
Capital represent only company's financial assets that are available to spend.
| Equity represents the total amount of money would receive if all the assets of business liquidated and paid off the company's debt.
|
Equity helps to determine company financial stability for long term.
| Capital determines whether a company can able to pay for the short-term production of products and services.
|
Equity represent the overall value of a business.
| capital focuses only on currently available financial resources
|


4 thoughts on “What is Equity in Business and Why Does It Always Matter”